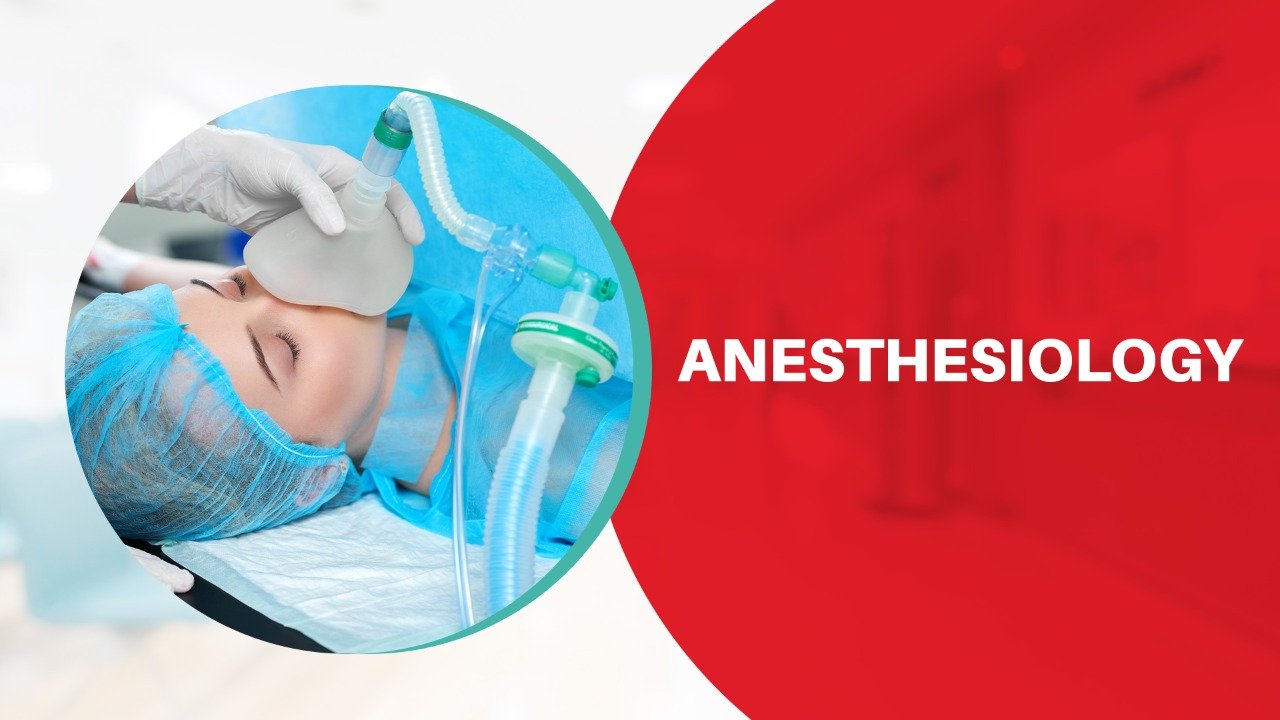
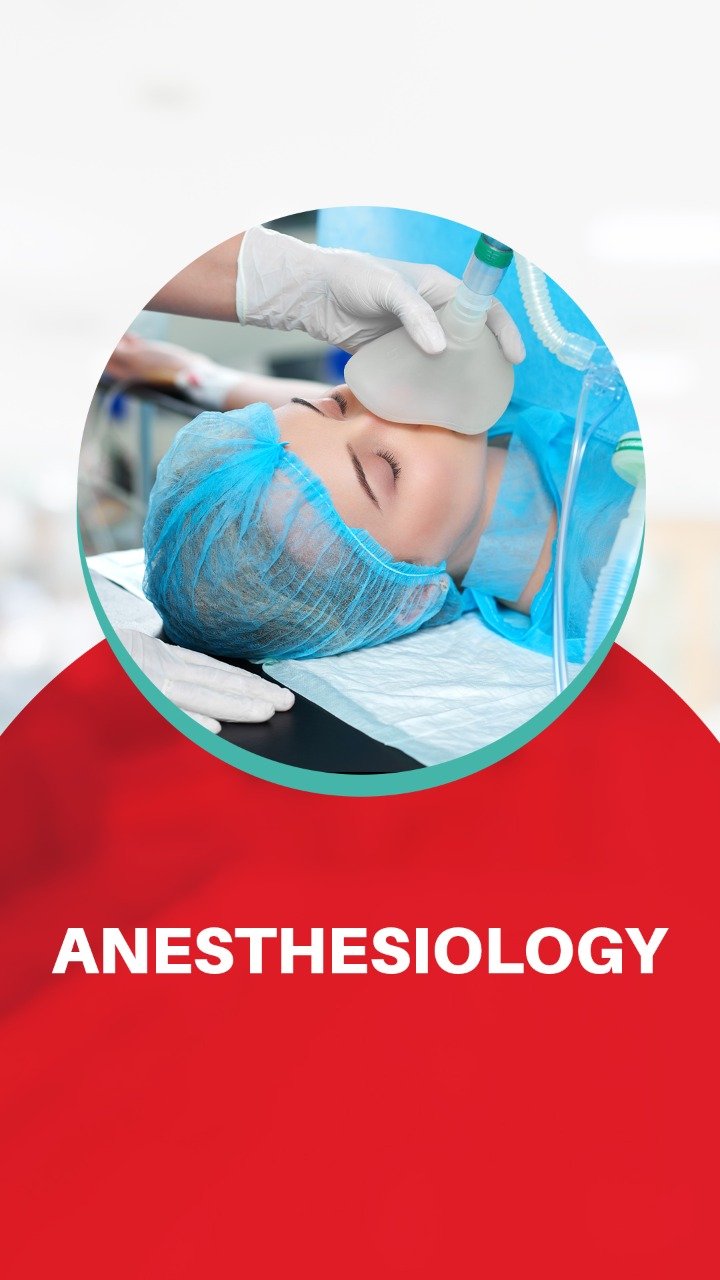
Anesthesiology is a type of medicine devoted to:
- Complete care for patients prior to, during, and aftersurgery;
- Critical medical care, and
- The treatment of chronic and acute pain.
- Labour Analgesia.
There are a variety of types of anesthesia available which include general anesthesia regional anesthesia and sedation anesthesia. The kind of anesthesia is chosen depends on the medical history of the patient as well as the procedure or procedure, as well as the preference of the patient.
What exactly is an anesthesiologist's job?
Anesthesiologists are responsible for the patient’s health before the, during and after surgery. An anesthesiologist does the following:
To Ensure pain free surgical procedure
- Check if it’s safe to go ahead with the anesthetic surgical procedure.
- Create an anesthetic treatment plan in consultation with patient.This can be generally anesthesia. It could be sedation, general or regional anesthesia, like a spinal epidural and regional block (usually with the intravenous administration of sedation).
- Make sure that you are unconscious using general anesthesia or the proper level of sedation anesthesia for sedation.
- Maintain and monitor the normal vital signs, such as respirations (breaths) as well as pulse blood pressure and temperature.
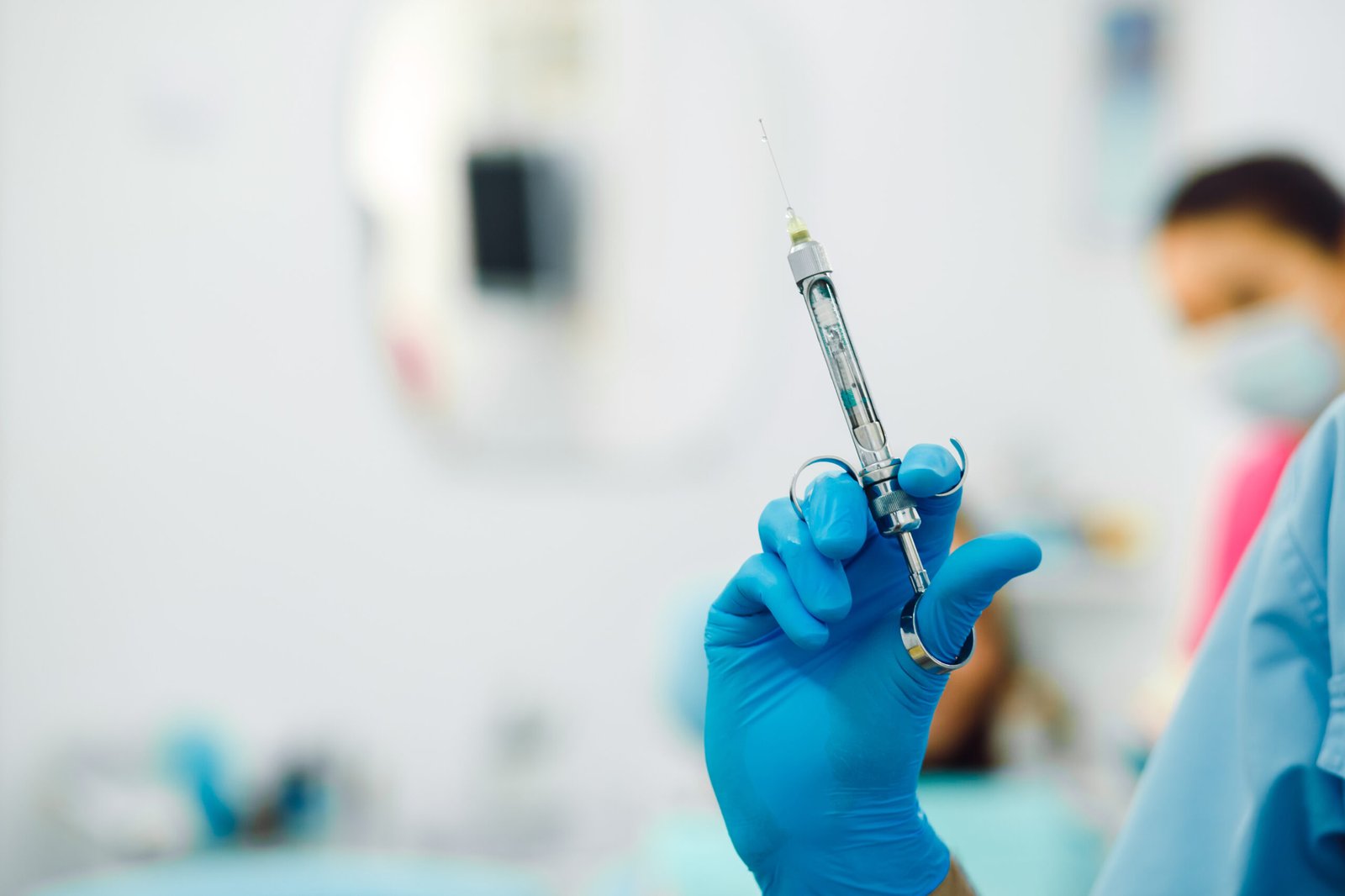
- Monitor and maintain the normal levels of oxygen in bloodstream as well as carbon dioxide gas that is in the lungs.
- Recognize and treat any health issue or emergency that might occur prior to, during, or following the procedure, for example, an unanticipated or allergic reaction to medication bleeding, an unanticipated change in vital indicators.
- Reduce the stress response to the procedure or operation to help the patient get the most effective recovery possible.
- Control pain after surgery.
- Continue to provide care following the procedure in the anesthesia care unit or the intensive care unit.
The anesthesiologist could collaborate with a licensed nurse anesthetist (CRNA) or residents, and trainee nurse anesthetist. Each of these providers are supervised by the anesthesiologist. The physician is the sole responsible for patient’s security.
Local Anesthesia
In the case of local anesthesia, only the surgical site is completely numb. Local anesthesia can be administered through spray or injection or even as an Ointment. You’ll be asleep or mildly asleep. Local anesthesia is commonly employed in outpatient procedures like hand or foot surgery. Dental offices and doctors’ offices generally employ this technique. The patient will return home the next day. There may be a feeling of an numbness or tingling in the area afterward.
Regional Anesthesia
The type of anesthesia is used to numb an area of your body like the lower body with epidural or spinal anesthesia, and also the extremity (arm or leg) that is anesthesia for nerve block. Examples of how regional anesthesia can be commonly used are spinal anesthesia to treat knee and hip replacement surgeries epidural anesthesia to help with birth, and nerve block anesthesia to treat wrist or shoulder surgery.
General Anesthesia
General anesthesia permits your operation or procedure to be carried out safely when you’re in deep sleep or asleep. The vital organs and your vital indicators will be checked and monitored when you’re under a general anesthetic. Additionally, you will receive pain medicine as well as your body’s stressful reaction in response to the procedure will be minimized as much as is possible. These steps will help speed your recovery following surgery.
You can lower the chance of receiving anesthesia by discussing these points to your anesthesiologist and your surgeon prior to the procedure:
- Health conditions ( such as hypertension or heart, lung or liver problems, diabetes).
- Your history of blood transfusions.
- If you have a history of depression or other mental illnesses.
- Recent surgeries and hospitalizations.
- You have experienced previous problems when you were anesthesiologist.
- Your dental background (loose tooth, crowns or bridges).
- The medications you are taking (prescription or over-the counter, or herbal).
- The medication you take and your food allergy experience.
- Your alcohol, tobacco and recreational drug past.
- Family members of blood who have experienced problems with anesthesia.
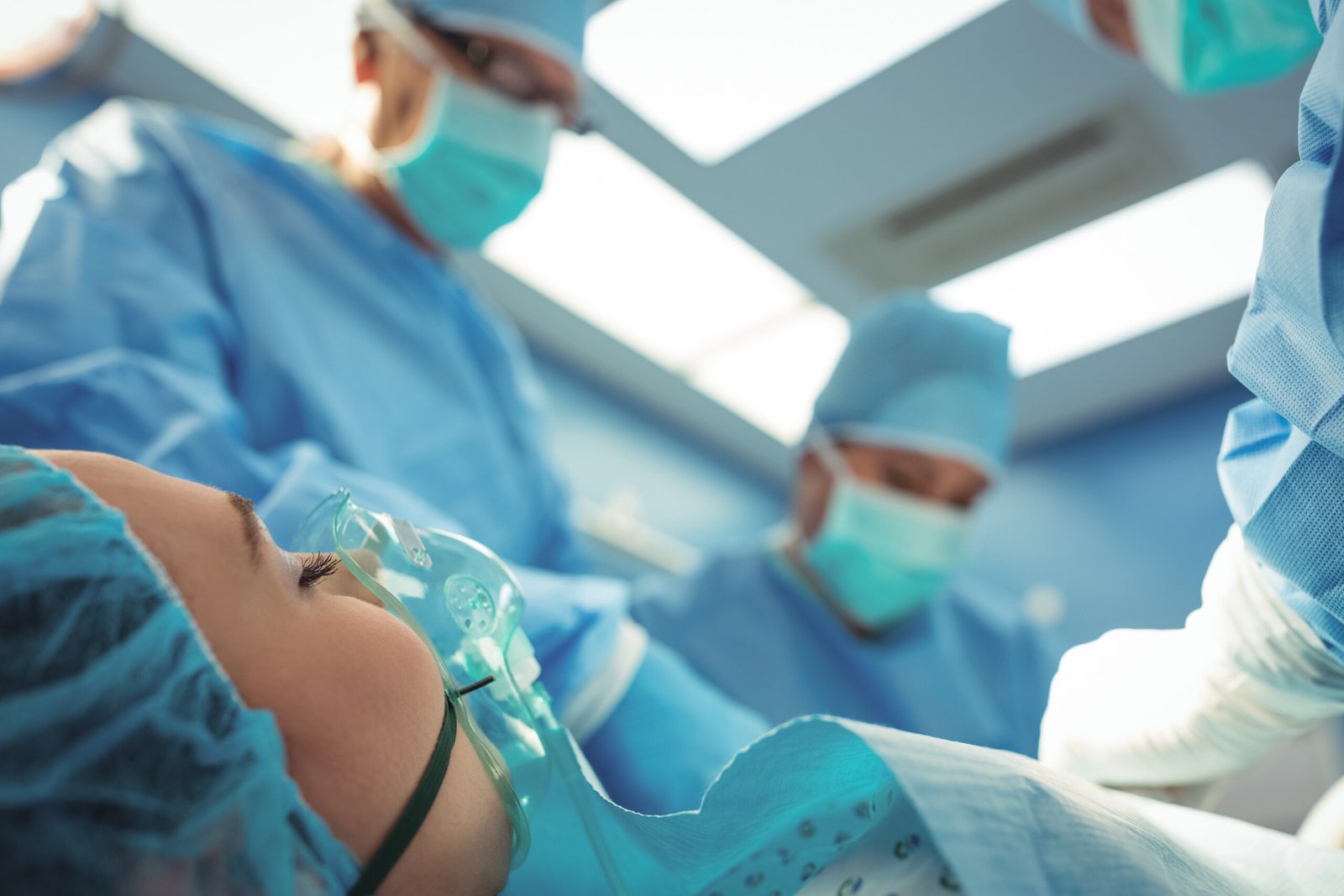
Consult Dr. Kailash Rathod , Anesthetist at Jankalyan Hospital for more information Anesthesia.

